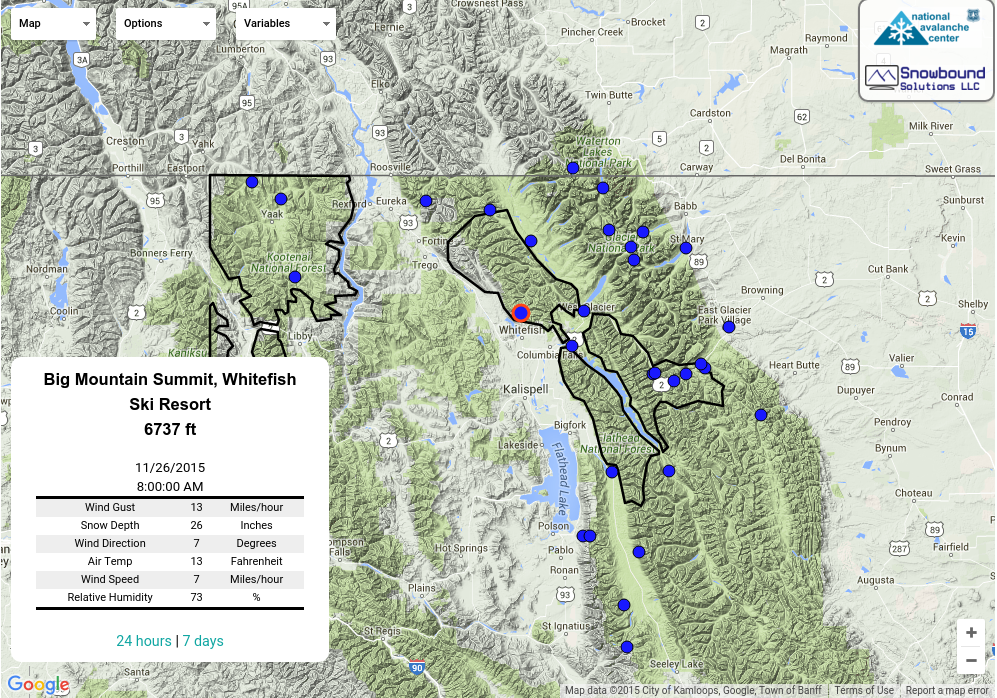
| Sunday | Sunday Night | Monday | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Cover: | Partly Cloudy | Mostly Cloudy | Mostly Cloudy |
| Temperatures: | 29 to 35 deg. F. | 20 to 25 deg. F. | 27 to 33 deg. F. |
| Wind Direction: | Southwest | Southeast | Southwest |
| Wind Speed: | 10 to 15 gusting to 30 | 10 to 12 gusting to 20 | 10 to 15 gusting to 35 |
| Snowfall: | 0" in. | 0" in. | 0" to 4" in. |
| Snow Line: | 4500' | 4000' | 3000' |
Flathead Range and Glacier National Park
How to read the forecast
Dangerous conditions persist where there is good snow coverage above about 5,000 feet. The higher you go, the greater the likelihood of triggered or natural wind slabs on leeward or cross-loaded slopes. Smaller avalanches may step down to deeper weak layers, resulting in dangerously large slides near the Divide. With high freezing levels, loose wet avalanches are likely on very steep terrain. Beware of shooting cracks and collapsing in stiffer snow and watch for rollerballs where the surface is wet.
3. Considerable
?
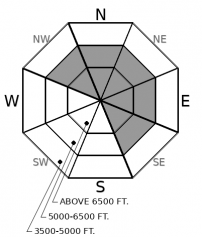
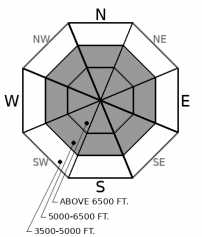
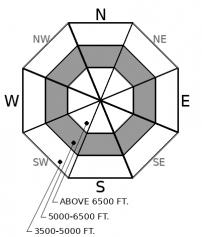
Above 6500 ft.
3. Considerable
?
5000-6500 ft.
1. Low
?
3500-5000 ft.
- 1. Low
- 2. Moderate
- 3. Considerable
- 4. High
- 5. Extreme
-
Type ?
-
Aspect/Elevation ?
-
Likelihood ?CertainVery LikelyLikelyPossible
 Unlikely
Unlikely -
Size ?HistoricVery LargeLargeSmall
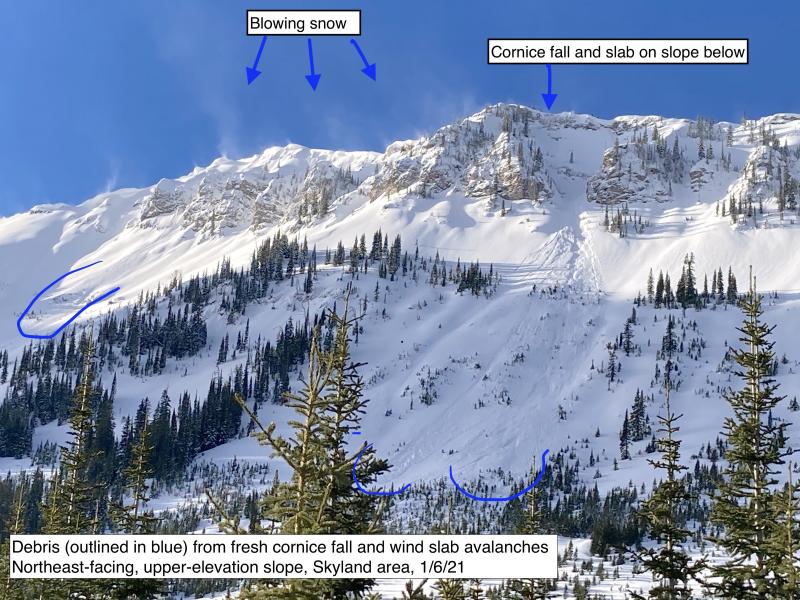
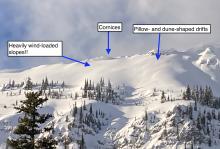
Winds from the south and southwest have been blowing snow across ridgelines and cross-loaded features for several days. Wind slab avalanches were reported in John F. Steven Canyon Saturday. Soft, recently formed slabs on the leeward side of these terrain features may break beneath you. Firmer slabs have to potential to break above you, making them harder to manage. Look for recent cornice formation and the rounded drifts below. Shooting cracks in stiff snow mean that you have wandered too close. The safer snow is in sheltered, lower-angled terrain.
-
Type ?
-
Aspect/Elevation ?
-
Likelihood ?CertainVery LikelyLikelyPossible
 Unlikely
Unlikely -
Size ?HistoricVery LargeLargeSmall

Very large avalanches broke across terrain features on crusts and facets near the ground recently in John F. Stevens canyon. A similar snowpack structure exists in the Lake McDonald area and near the Flathead crest. These are the same zones that received the most loading during the recent storm. Flattop Mountain picked up 4.7” of water weight through yesterday. Avalanches that break under that strain, or the added stress of your weight, could be very dangerous. They can be triggered from a distance or from below where the snowpack is shallower. Approach alpine starting zones and the tracks of avalanche paths with caution. The safest bet is to minimize your exposure to terrain steeper than about 30 degrees. Collapsing, deep shooting cracks, or recent natural avalanches should only confirm your conservative terrain choices. Don’t wait to change your mind until after you’re in harm’s way.
-
Type ?
-
Aspect/Elevation ?
-
Likelihood ?CertainVery LikelyLikelyPossible
 Unlikely
Unlikely -
Size ?HistoricVery LargeLargeSmall

After 2 nights without refreezing, the snow is wet up to about 6,000 feet. On steep mid elevation slopes, rollerballs and small natural sluffs are clues that you can trigger loose wet avalanches. Shallow snow cover and rocky areas are likely trigger points. Pay attention even as you gain elevation. If the snow is saturated, it can slide. Even small sluffs above terrain traps can be dangous business.
Since Friday’s storm, precipitation has mostly dried up across the region, but warm air continues to stream in from the southwest. Avalanches have come in a variety of flavors in recent days. Skiers and explosives triggered small storm slabs in the Whitefish Range, and large persistent slab avalanches broke near the ground on wind-loaded slopes in John F. Stevens Canyon.
Warming, wind-drifted snow, and storm snow have combined to create the potential for an array of avalanche problems. The danger is different in different zones, and even across zones, but the only green light is where there is little or no snow. You can trigger large slabs of new and drifted snow, or avalanches that break near the ground on weak facets and crusts that formed earlier this season. Natural and remotely-triggered avalanches are also possible, particularly in the eastern part of the forecast region. And to top it off, above-freezing temperatures make triggering small wet loose avalanches possible; these could leave you tangled in the bush under heavy debris.
Make careful assessments before committing to steep, open terrain. Be more conservative the further east and north you go – and the higher in elevation.
Warm southwesterly flow will continue today with gusty ridgetop winds and high freezing levels. A minor cold front tonight will lower temperatures and make light snow possible in the mountains.
This forecast applies only to backcountry areas outside established ski area boundaries. The forecast describes general avalanche conditions and local variations always occur. This forecast expires at midnight on the posted day unless otherwise noted. The information in this forecast is provided by the USDA Forest Service who is solely responsible for its content.