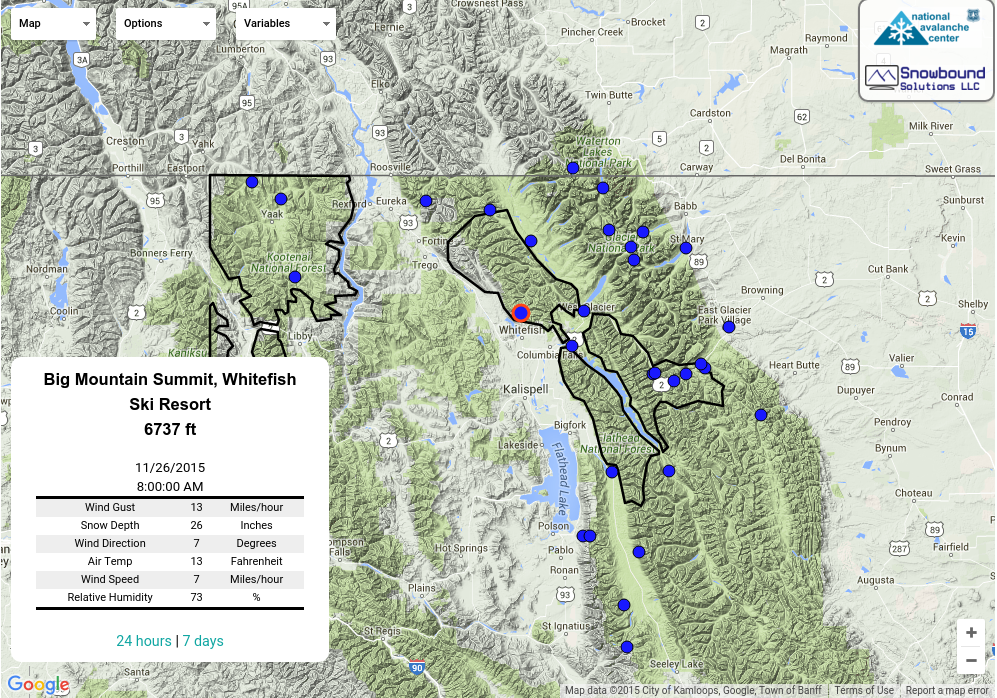
| Thursday | Thursday Night | Friday | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Cover: | Mostly Cloudy | Mostly Cloudy | Partly Cloudy |
| Temperatures: | 22 to 27 deg. F. | 13 to 18 deg. F. | 24 to 31 deg. F. |
| Wind Direction: | West | West | West |
| Wind Speed: | 5 to 10, gusting to 20 | 5 to 10 | 5 to 10 |
| Snowfall: | 0" in. | 1" to 2" in. | 0" in. |
| Snow Line: | 2000' | 2000' | 1500' |
Whitefish Range
How to read the forecast
Be alert for isolated avalanche hazards on steep, upper-elevation terrain. These mostly involve recently-formed slabs of drifted snow on leeward and cross-loaded slopes. They will be small but dangerous above terrain traps. Be alert for clues to exceptions to the mostly stable conditions - shooting cracks, whumpfing, hard but hollow-feeling drifts, and, as always, recent natural or triggered avalanches.
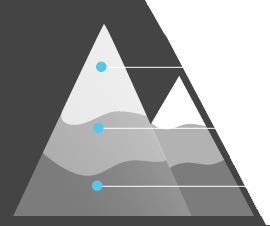
1. Low
?
Above 6500 ft.
1. Low
?
5000-6500 ft.
1. Low
?
3500-5000 ft.
- 1. Low
- 2. Moderate
- 3. Considerable
- 4. High
- 5. Extreme
-
Type ?
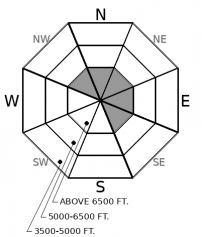
-
Aspect/Elevation ?
-
Likelihood ?CertainVery LikelyLikelyPossible
 Unlikely
Unlikely -
Size ?HistoricVery LargeLargeSmall
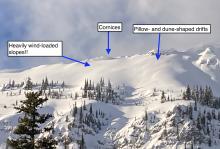
Be cautious around steep start zones with recently-formed slabs of drifted snow. These are isolated and mostly consist of soft pockets of low-density snow created in the past day or two. In the most wind-exposed terrain, you might find a few hard, hollow-feeling drifts that formed over the weekend. Both flavors are isolated and tough to release, particularly the older but thicker slabs. Both can be dangerous if they push you into or over a terrain trap that amplifies the chances for injury or deeper burials.
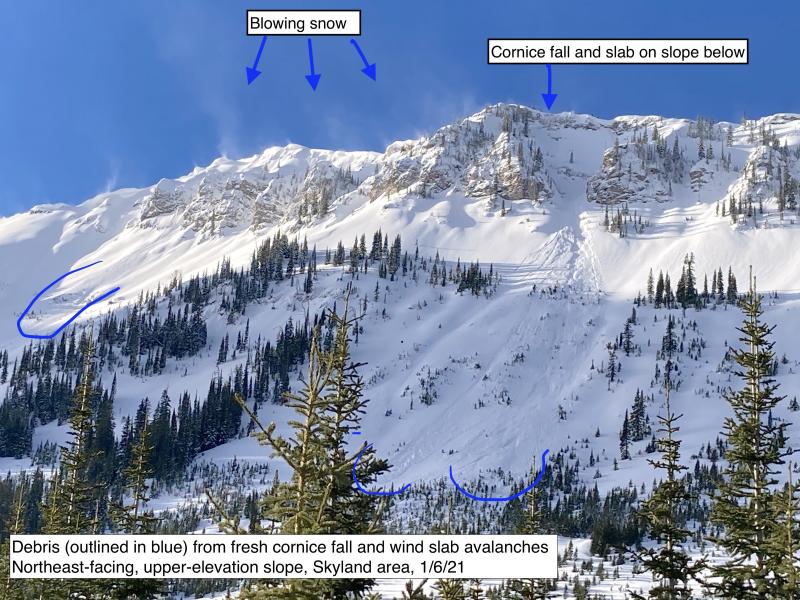
Today's avalanche hazards primarily involve the near-surface layers of the snowpack. They'll mostly break near the interface with the 2/1 crust, and their size and type depend on the amount of recent and drifted snow that's accumulated above the crust. The largest slides will involve slabs of drifted snow that can be one to two feet thick. Neither Zach nor I found many examples of this hazard in the Flathead Range and Stevens Canyon on Wednesday (example 1, example 2). But recent winds have been gusty, so expect this hazard on isolated leeward and cross-loaded slopes at upper elevations. They may be more widespread in the Swan Range, which has picked up more snow in the past three days.
On very steep terrain yesterday, I was able to trigger Loose Dry avalanches that ran on the very hard 2/1 crust. With only about 3 inches of snow above the crust, they were harmless. They might pose a danger where you find more than about 8 inches of new snow on the crust. Again, those conditions will likely be more widespread in the Swan Range.
The 2/1 crust is stout and extends to at least 7000 feet. It's a few inches thick at low and mid elevations. It's hard enough to cap the snowpack and limit if not eliminate the potential for collapsing weak layers below it, of which there aren't many. That's not a license to ride anything; there are some caveats. It's thinner and more fragile underfoot above about 6500 feet, and thus there are isolated spots where a person's weight could affect weak layers beneath it at upper elevations. In addition, the weakest snow I've found recently is in the few inches of snow below the crust. The takeaways are to be alert for whumpfing collapses and to adjust your routes to avoid the runouts of steep start zones as you climb above about 6500 feet.
The second caveat involves the very serious Deep Persistent Slab problem, which seems confined to steep, shaded slopes at upper elevations in the Flathead Range and Glacier National Park. That's terrain that harbors crust and facet combinations near the ground that were developed early season and which have persisted since. These are unreactive except on isolated slopes without the contributing factors of rain and abrupt temperatures swings. They might release with large triggers, like falling cornices, or small triggers in thin spots in the slab, like you. Given that getting caught in one is very likely unsurvivable, it pays to avoid being under slopes that are likely to harbor the weak layer, even if the 2/1 crust limits your chances of collapsing layers beneath you.
We're on the banks of the atmospheric river, maybe even out of the floodplain. Most of today's precipitation will be south of our region, though the southern Swan Range and the Stevens Canyon/ Marias Pass area may wring out a few inches of new snow. Winds look to be light with moderate gusts and westerly. Temperatures remain cool. A system Friday night and Saturday may bring more snow.
This forecast applies only to backcountry areas outside established ski area boundaries. The forecast describes general avalanche conditions and local variations always occur. This forecast expires at midnight on the posted day unless otherwise noted. The information in this forecast is provided by the USDA Forest Service who is solely responsible for its content.